JCM | Free Full-Text | MicroRNA Expression Relating to Dietary-Induced Liver Steatosis and NASH | HTML
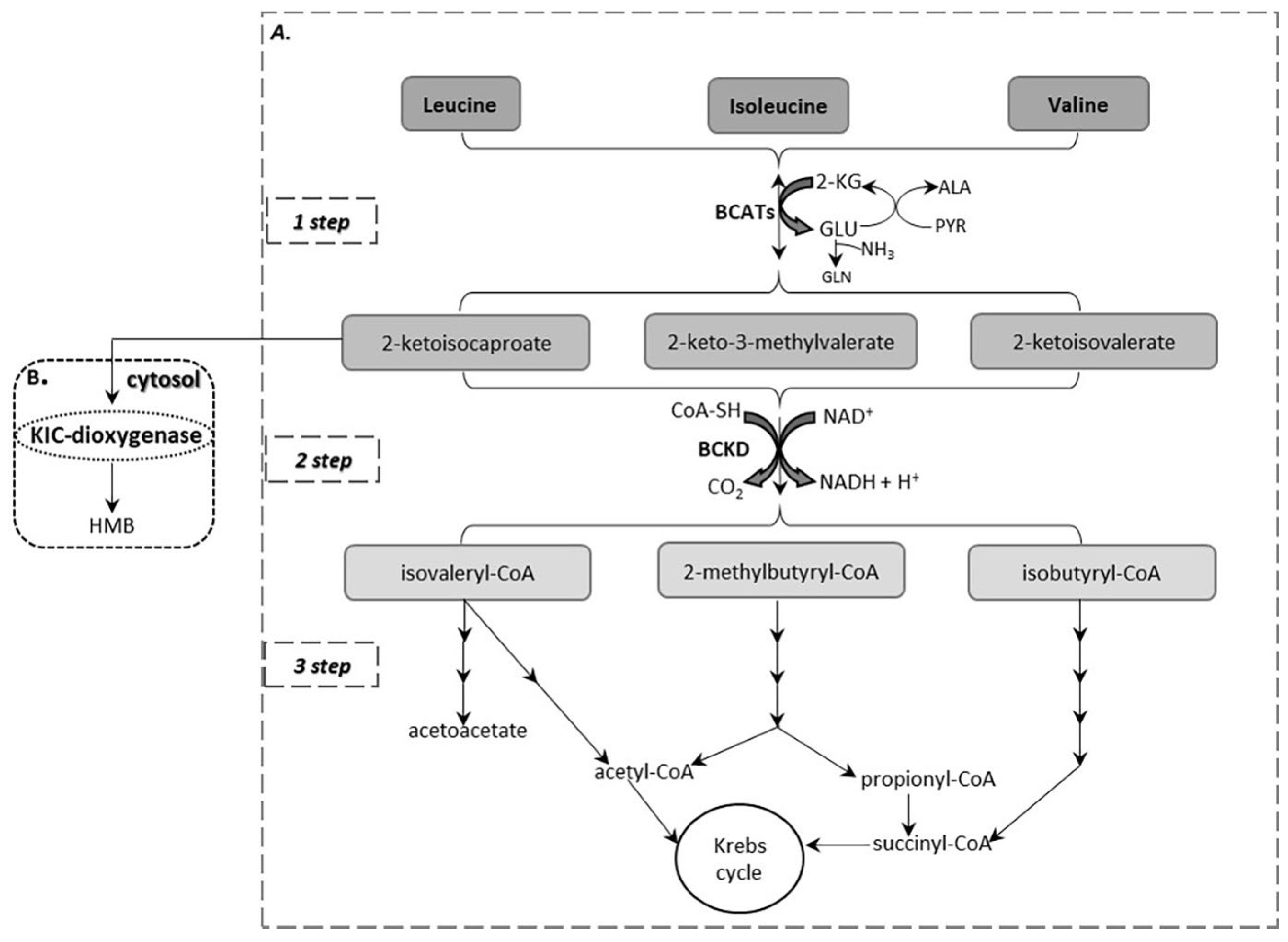
IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Critical Role of the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Catabolism-Regulating Enzymes, Branched-Chain Aminotransferase (BCAT) and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKD), in Human Pathophysiology

Effects of BCAA supplementation on liver tumorigenesis in C57BL/6J mice... | Download Scientific Diagram

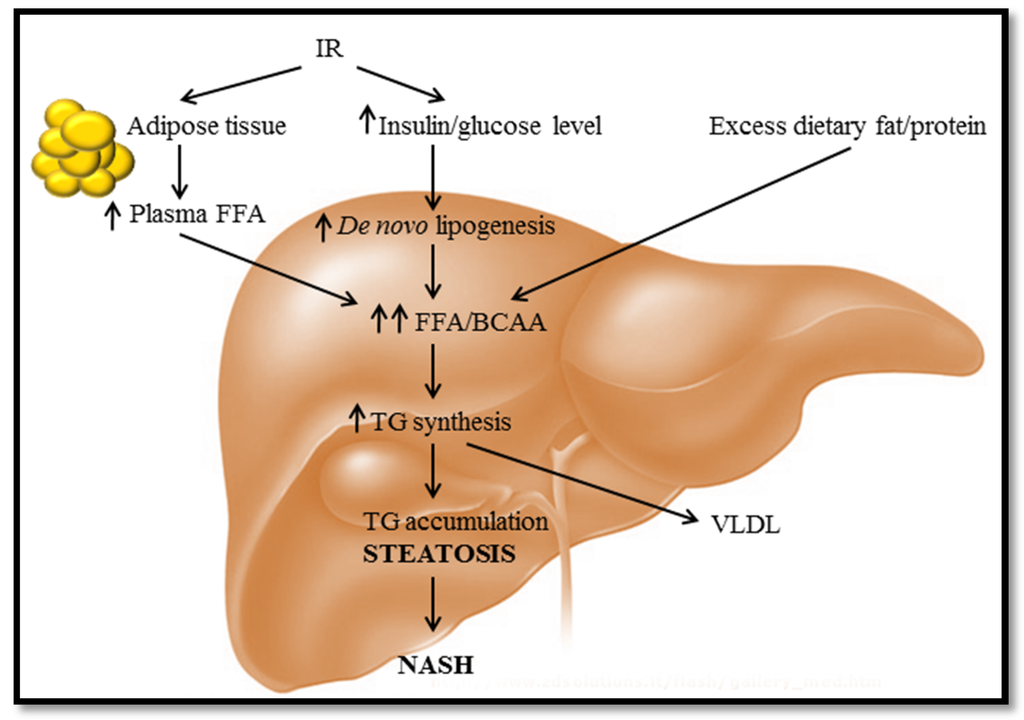
Branched Chain Amino Acids Cause Liver Injury in Obese/Diabetic Mice by Promoting Adipocyte Lipolysis and Inhibiting Hepatic Autophagy - ScienceDirect

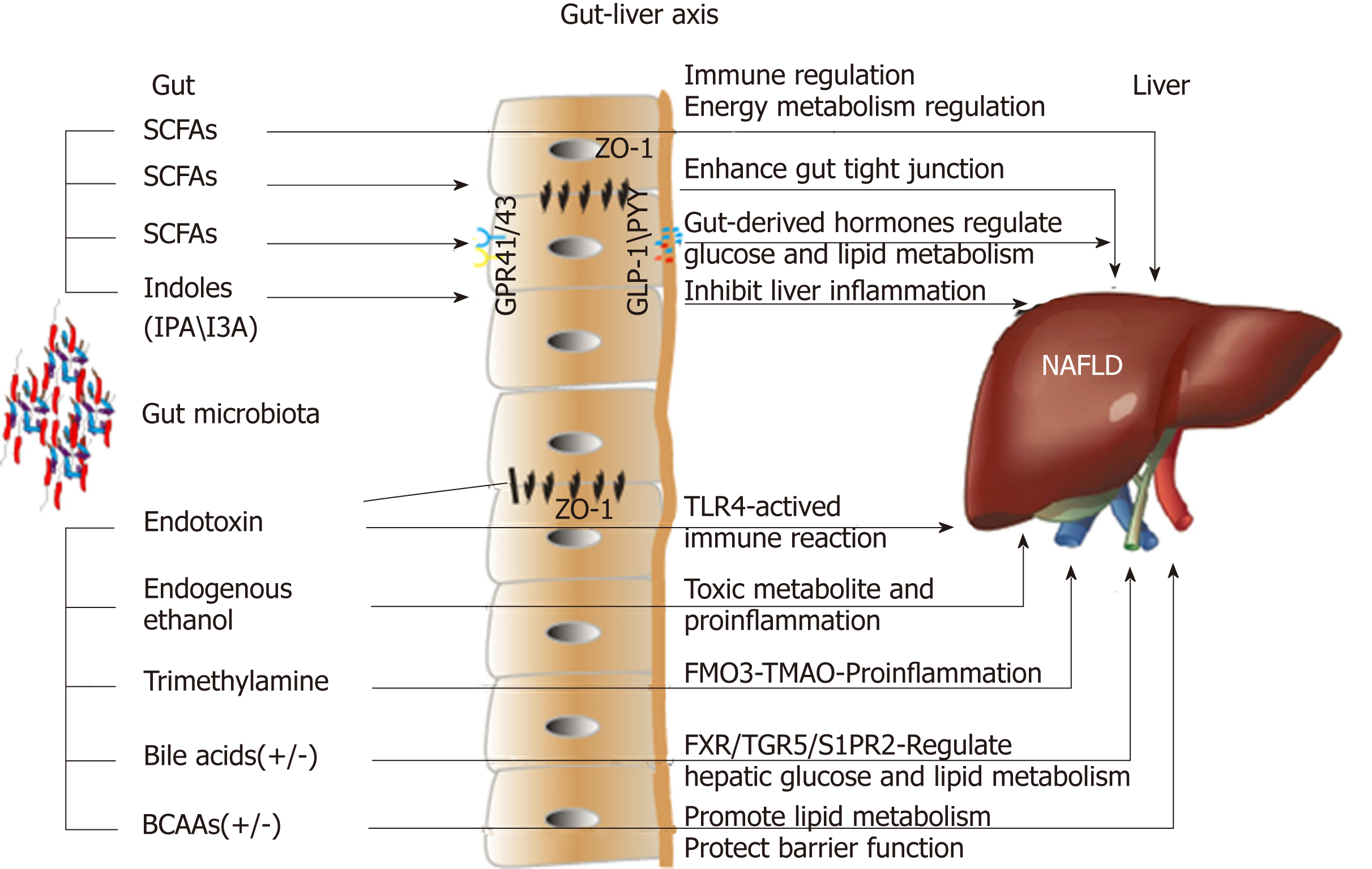
Gut microbiome-targeted therapeutic strategies against nonalcoholic... | Download Scientific Diagram
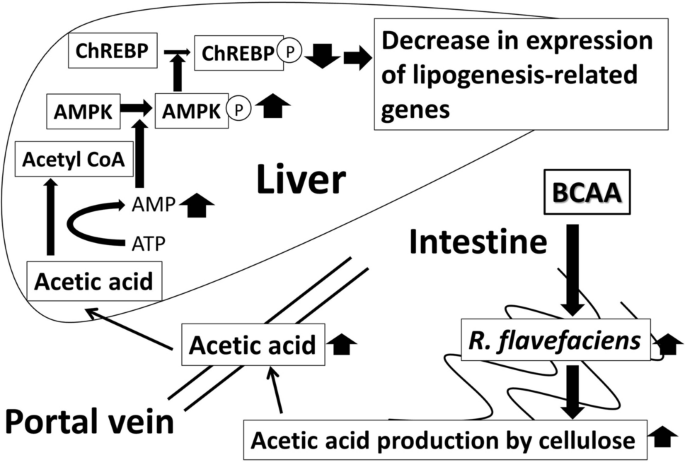
Supplementation of branched-chain amino acids decreases fat accumulation in the liver through intestinal microbiota-mediated production of acetic acid | Scientific Reports

Muscle-Liver Trafficking of BCAA-Derived Nitrogen Underlies Obesity-Related Glycine Depletion - ScienceDirect

Dietary protein insufficiency: an important consideration in fatty liver disease? | British Journal of Nutrition | Cambridge Core
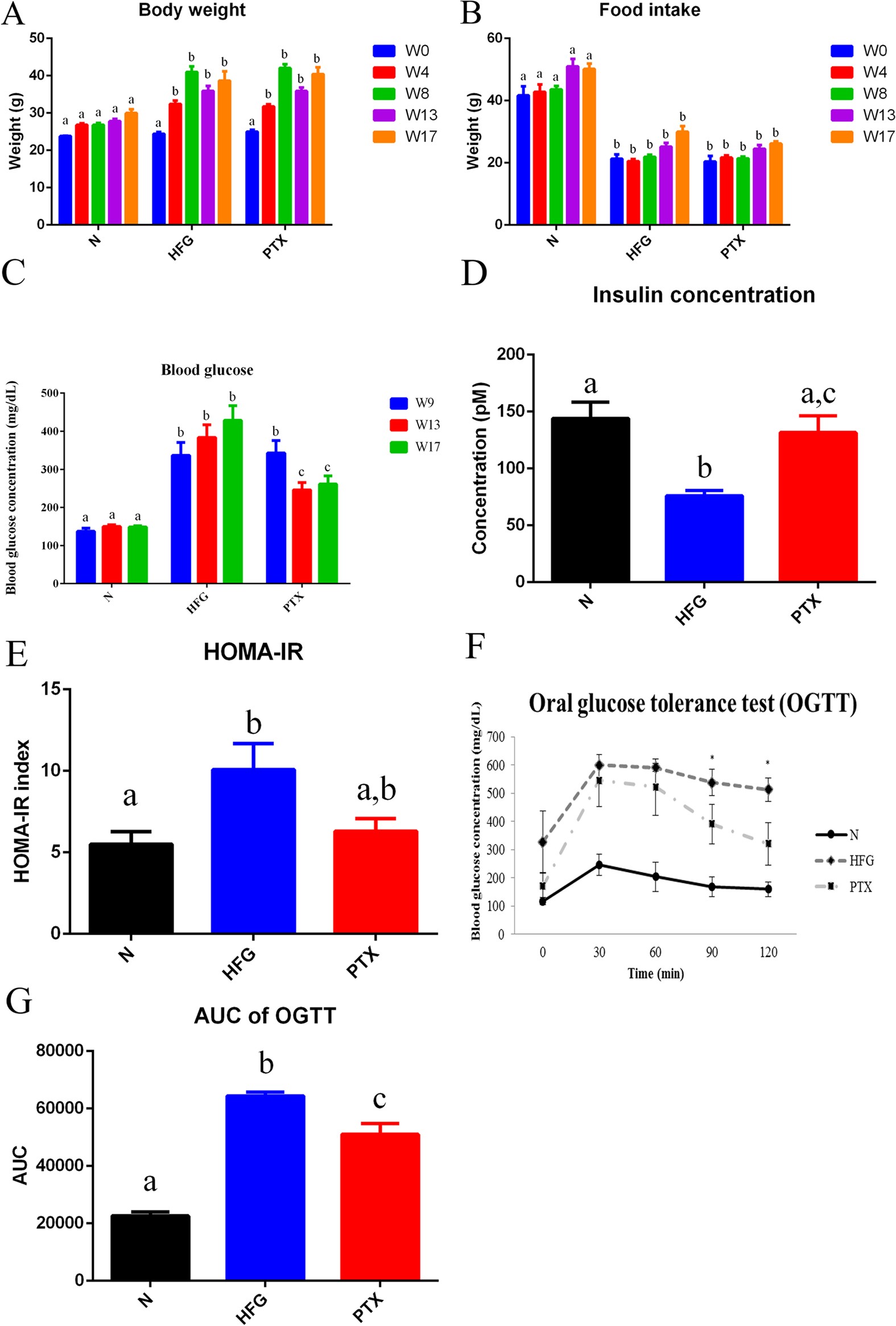
Pentoxifylline ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in hyperglycaemic and dyslipidaemic mice by upregulating fatty acid β-oxidation | Scientific Reports

Relationship of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction | JACC: Basic to Translational Science

Branched Chain Amino Acids Cause Liver Injury in Obese/Diabetic Mice by Promoting Adipocyte Lipolysis and Inhibiting Hepatic Autophagy - ScienceDirect

Comparison of liver, muscle and fat in BCAA metabolism and the effect... | Download Scientific Diagram
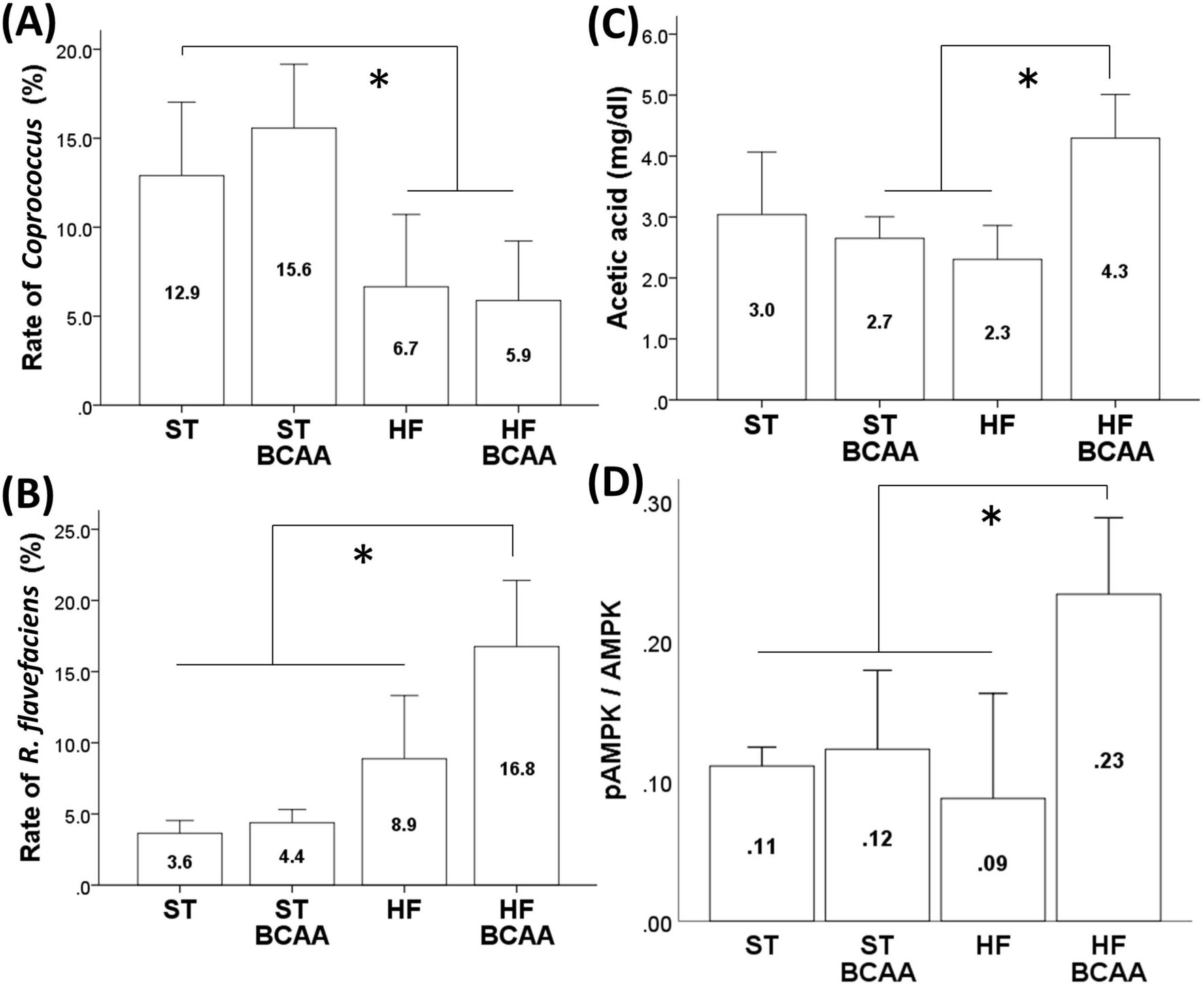
Supplementation of branched-chain amino acids decreases fat accumulation in the liver through intestinal microbiota-mediated production of acetic acid | Scientific Reports

Branched Chain Amino Acids Cause Liver Injury in Obese/Diabetic Mice by Promoting Adipocyte Lipolysis and Inhibiting Hepatic Autophagy - ScienceDirect
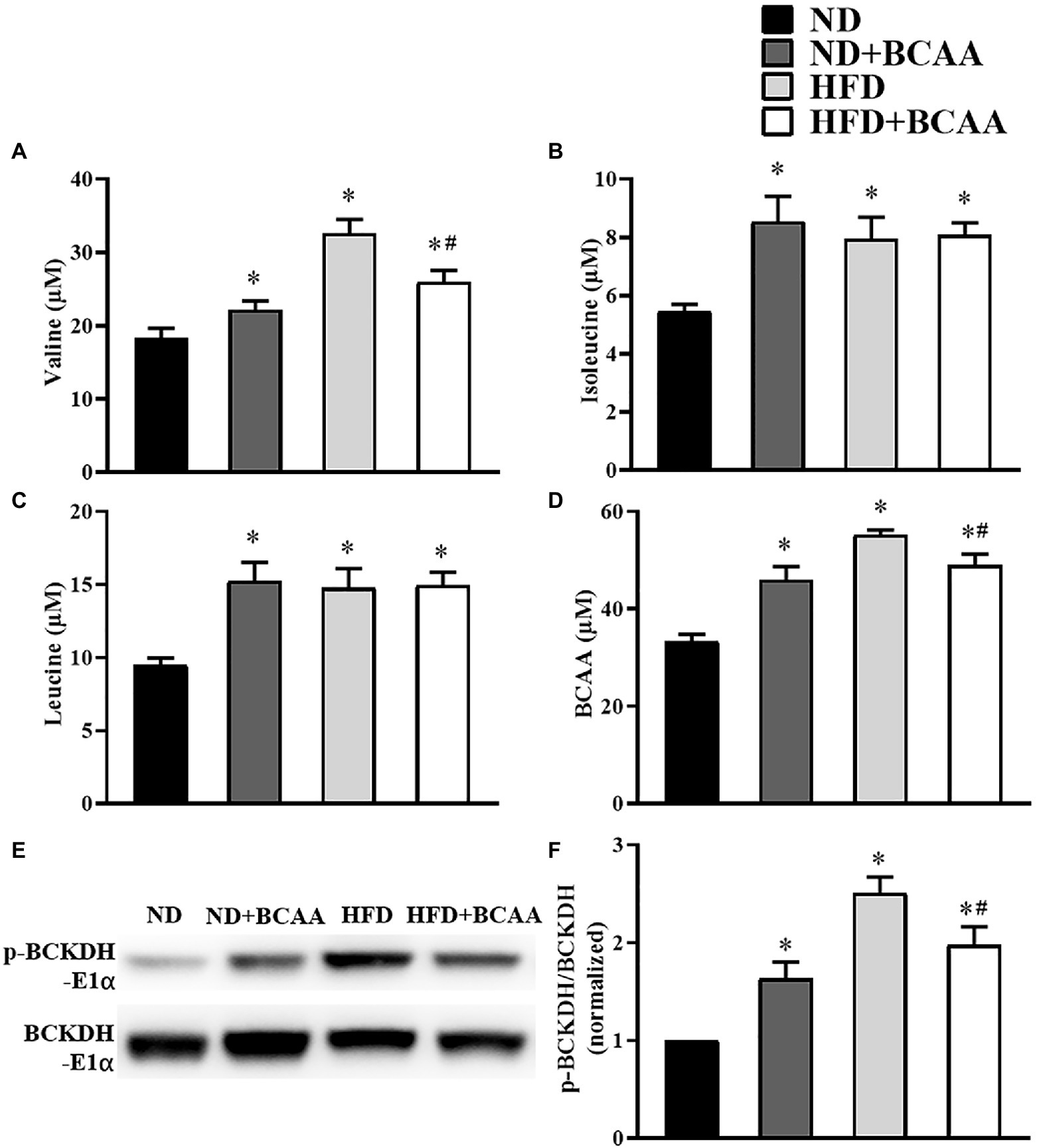
Frontiers | Oral administration of branched-chain amino acids ameliorates high-fat diet-induced metabolic-associated fatty liver disease via gut microbiota-associated mechanisms